An object is symmetric if it can be divided into two or more identical pieces that are arranged in an organized fashion. This means that an object is symmetric if there is a transformation that moves individual pieces of the object but doesn't change the overall shape. The type of symmetry is determined by the way the pieces are organized, or by the type of transformation:
- An object has reflectional symmetry (line or mirror symmetry) if there is a line going through it which divides it into two pieces which are mirror images of each other.

Example to practice in Primary Education:

- An object has rotational symmetry if the object can be rotated about a fixed point without changing the overall shape.

Example to practice in Primary Education:

- An object has translational symmetry if it can be translated without changing its overall shape.
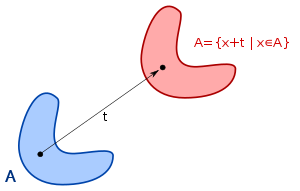
Example to practice in Primary Education:

- An object has helical symmetry if it can be simultaneously translated and rotated in three-dimensional space along a line known as a screw axis.




No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario